Many people believe that smartphones are somehow less of a target for threat actors. They couldn’t be more wrong.
Bitdefender Labs warns that cybercriminals are doubling down on spreading malware through Meta’s advertising system. After months of targeting Windows desktop users with fake ads for trading and cryptocurrency platforms, hackers are now shifting towards Android users worldwide.
Bitdefender researchers recently uncovered a wave of malicious ads on Facebook that lure targets with promises of a free TradingView Premium app for Android. Instead of delivering legitimate software, the ads drop a highly advanced crypto-stealing trojan — an evolved version of the Brokewell malware.
This campaign shows how cybercriminals are fine-tuning their tactics to keep up with user behavior. By targeting mobile users and disguising malware as trusted trading tools, attackers hope to cash in on the growing reliance on crypto apps and financial platforms.
Inside the Malicious Ad Campaign Targeting Android Users
According to our most recent analysis, the malware campaign (which is still active) made use of at least 75 malicious ads since 22 July 2025. By August 22, the ads have reached tens of thousands of users in the EU alone.


The ads used TradingView’s branding and visuals to trick people into downloading the free premium app onto their devices.


We’ve even spotted a variation of the ad pairing the TradingView branding with an image of a Labubu.

Note: If a desktop user, who does not fall in the targeted group, clicks on the ad, random, benign content will be delivered instead.

However, Android users who followed the link are redirected to a cloned webpage that mimics the official TradingView site (new-tw-view[.]online), where they unknowingly downloaded a malicious .apk file from tradiwiw[.]online/tw-update.apk.

The file has the MD5 checksum 788cb1965585f5d7b11a0ca35d3346cc, and it drops the packed APK 58d6ff96c4ca734cd7dfacc235e105bd.
Once installed, the app immediately begins requesting powerful permissions such as accessibility access — all while hiding behind fake update prompts.


The dropped application asks for accessibility, and after receiving it, the screen is covered with a fake update prompt. In the background, the application is giving itself all the permissions it needs.
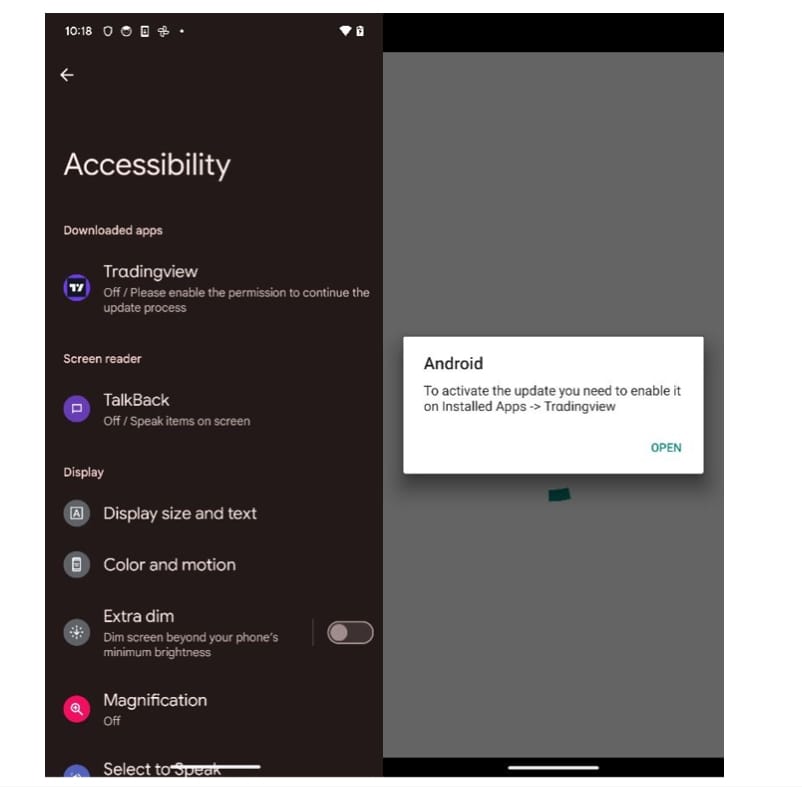
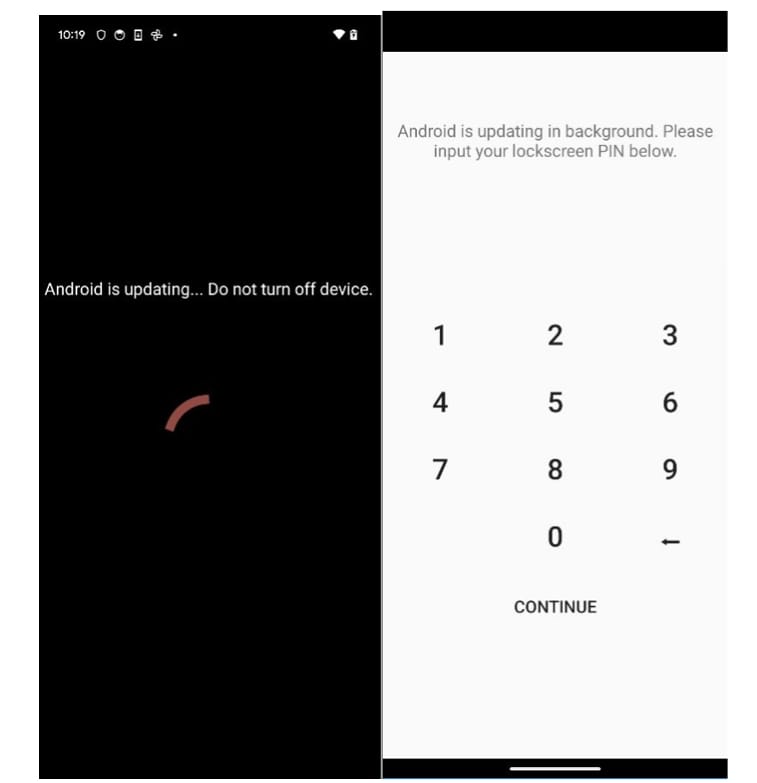
The application also tries to trick the user into giving their lock screen PIN:
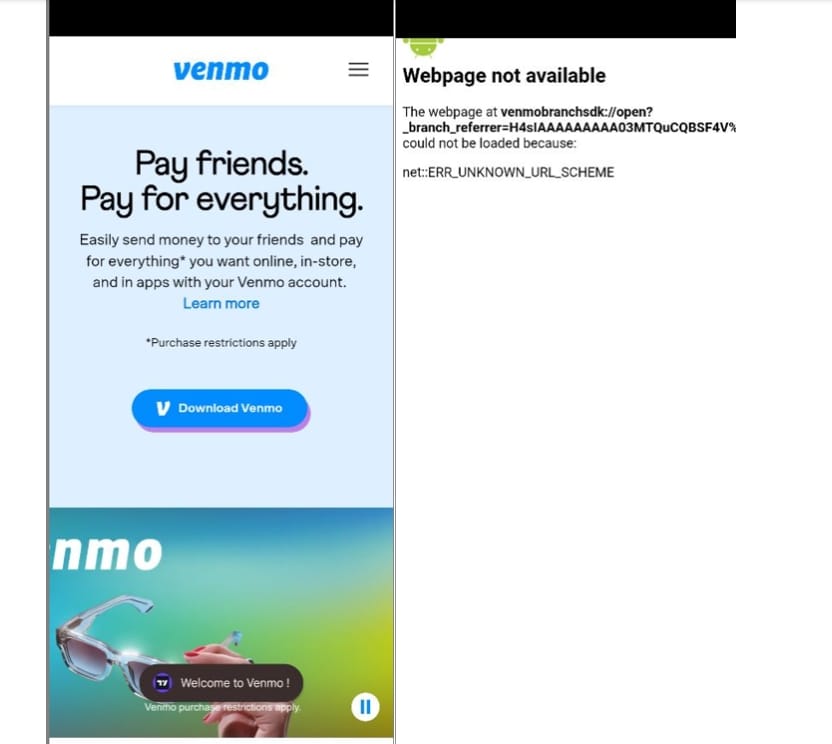
The application chooses to overlay over some installed apps, such as YouTube, where a WebView and a Toast message is displayed, prompting the user to download the Venmo app:
The initial application decrypts from its resources the dropped application and starts it by prompting the user to give it accessibility permissions, since the dropped app does not have a launcher. If the user grants these permissions, the dropper is uninstalled to cover its tracks.
By decrypting the strings used in the classes, we find permissions requests in multiple languages available, such as English, Spanish, Portuguese, German, French, Italian, Turkish, Finnish, etc.
Once installed, the malware reveals itself as far more than a simple credential stealer. It’s an advanced version of the Brokewell malware, a full-fledged spyware and remote access trojan (RAT) with a vast arsenal of tools designed to monitor, control, and steal sensitive information from the victim’s device.
Its capabilities include:
- Crypto theft – Scanning for BTC, ETH, USDT, IBANs, and more.
- 2FA bypass – Scraping and exporting codes from Google Authenticator.
- Account takeover – Providing the possibility to overlay fake login screens
- Surveillance – Recording screens, keylogging, stealing cookies, activating the camera and microphone, and tracking live location.
- SMS interception – Hijacking the default SMS app to intercept messages, including banking and 2FA codes.
- Remote control – Communicating with attackers over Tor and WebSockets, with commands to send SMS, place calls, uninstall apps, or even self-destruct.
In short, this is one of the most advanced Android threats seen in a malvertising campaign to date.
The app is obfuscated and uses two native libraries to retrieve what methods to execute and the parameters to call them with. It also contains methods to search for regexes of crypto wallets such as:


The dropped application contains 2 raw files which are used as:
– A configuration file that is loaded as a JSON and which contains what websites to use for overlaying installed apps on the device.

– The other one is a .dex file stored as a raw resource file, which is decrypted using a key from the native library and its classes are loaded using reflection. This is where most of the malicious code is hidden.
The application connects to a Tor server and a WSS one for C2C communication and logging.
Extended supported commands:
|
Commands |
|
do_SET_DEFSMS_APP |
|
revert_DEF_SMS_APP |
|
only_hide_DEF_SMS_APP |
|
doRUN_JS_WEBVW |
|
estabWSOCK_APK_SHELL |
|
doGETCLIPBOARDVAL |
|
doDUMPCOOKIESTXT |
|
doDUMPKEYLOGTXT |
|
doDUMPPUSHNOTIFTXT |
|
doCSTSHOT |
|
doSHOWTOAST |
|
doPING |
|
doINIT |
|
getInstalledPackages |
|
checkIPexit |
|
getBattery |
|
runSHELL |
|
setC2addr |
|
setwsockC2addr |
|
do_ADD_CONTACT |
|
showNotif |
|
showOVLAY |
|
doCustomShowOVLAY |
|
doClearOVLAY |
|
AcsDumpCurrentNode |
|
openCertainAPK |
|
ToggleNotifCertainAPK |
|
readLOCKPIN |
|
scrape_GOOGLE_AUTHENTICATOR |
|
export_GOOGLE_AUTHENTICATOR |
|
export_bycoord_GOOGLE_AUTHENTICATOR |
|
scrape_GMAIL_last_inbox |
|
scrape_YAHOO_last_inbox |
|
scrape_OUTLOOK_last_inbox |
|
turnon_DEVMODE_feature |
|
turnon_byelem_DEVMODE_feature |
|
steal_GMS_PASSWD |
|
doOneShotCamFront |
|
doStreamCamFront |
|
doOneShotCamBack |
|
doStreamCamBack |
|
doStopCamServices |
|
start_VNC_smallshot |
|
stop_VNC_smallshot |
|
doSet_IBAN_NUM |
|
doGet_IBAN_NUM |
|
doClear_IBAN_NUM |
|
doSet_USDT_TRC20 |
|
doGet_USDT_TRC20 |
|
doClear_USDT_TRC20 |
|
doSet_BTC_ADDR |
|
doGet_BTC_ADDR |
|
doClear_BTC_ADDR |
|
doSet_ETH_ADDR |
|
doGet_ETH_ADDR |
|
doClear_ETH_ADDR |
|
do_run_uninstallAVseq |
|
do_SOCKS5_start_server |
|
do_SOCKS5_stop_server |
|
do_SSH_PORT_FWD |
|
openWebvwC2Inject |
|
askC2_LOCKPIN |
|
askC2_PERMIT |
|
checkPERMIT |
|
simulateVIBRATE |
|
zeroVOLUME |
|
zeroBRIGHTNESS |
|
doSendSMS |
|
doPhoneCall |
|
doUninstallPKG |
|
DO_download_URL_to_fname |
|
DO_install_apk_file |
|
setInjectList |
|
GetJSONInjectList |
|
ClearInjectList |
|
ClearInjectBypassList |
|
doEnableUnknownSourceInstall |
|
doRecordAudio |
|
doStartProjection |
|
doStopProjection |
|
doScreenshot |
|
doClickElem |
|
doClickXY |
|
doSwipeXY |
|
doDrawXY |
|
doTypingElem |
|
doScrollElem |
|
doGetGeoloc |
|
DO_live_loc_routine |
|
DO_stop_liveloc_routine |
|
doCheckKeyguardState |
|
doHideIcon |
|
doHideFKLCRIcon |
|
doUnHideIcon |
|
doUnHideFKLCRIcon |
|
doEnabAggressiveReconnect |
|
doDisabAggressiveReconnect |
|
doWakeScreen |
|
doPINAutoUnlockScreen |
|
doPATTERNAutoUnlockScreen |
|
doPASSWDAutoUnlockScreen |
|
openDeveloperOptions |
|
doGetCallHistory |
|
doActivateAdminPermit |
|
doOpenNotifSettings |
|
doStopAcsSrvc |
|
doSelfDestroy |
|
doFlipANTI_UNINSTALL |
|
doGetPKGINFO |
|
doSetAggressiveACSMASK |
|
doSetAssertiveACSMASK |
|
doGetRAMconsumed |
|
DoGlobalActionHome |
|
DoGlobalActionBack |
|
DoGlobalActionRecents |
|
DoGlobalActionNotifications |
|
DoGlobalActionPWRdialog |
|
DoGlobalActionLockScreen |
|
DoGlobalActionTakeScreenshot |
|
DoGlobalActionDpadCenter |
|
DoGlobalActionDpadDown |
|
DoGlobalActionDpadLeft |
|
DoGlobalActionDpadRight |
|
DoGlobalActionDpadUp |
|
DoGlobalActionSplitScreen |
|
DoSwipeUp |
|
DoSwipeBottom |
|
DoSwipeRight |
|
DoSwipeLeft |
|
DumpTelephonyInfo |
|
DUMP_telephony_2ndsim |
|
doRUN_TOR_ONION |
|
doGET_TOR_INFO |
|
doGET_TOR_RC |
|
doCHECK_TOR |
|
doREACH_TORC2 |
IOCs analyzed dropper samples downloaded from the Facebook ads:
|
39669a3663829b380c7a776857021ac8a325cf6c0f709dd502f5f0a0945da953 |
|
6dd93a18b00db0f16042cd95ed45227aca0f850844e1cb9923e83df405757660 |
IOCs analyzed dropped samples:
|
78b3db9b68a4b62c6c4fffdcf0d0125aca464dbb4a6ef3526ac7c7ea1cfe88e4 |
|
66b5cf0fe3eb2506ce38701acabc242323e1cdbdb2b0a96909936477e03e0cf3 |
A Global, Multi-Language Scam
This Android wave is just one branch of a much larger malvertising operation abusing Facebook Ads that initially began targeting Windows desktops. Over time, the cybercriminals behind the campaign have impersonated dozens of well-known brands, people, and cryptocurrencies, including:
- TradingView, Binance, Bitget, Bitso, Blackbull and Bybit
- Chatbox, EToro, Exness and Grass (https://www.grass.io/)
- Facebook and Telegram
- FTMO, HTX, Hyper and GMGN
- LBank, Ledger, Lemon.me and Line
- Metatrader, Monad, Monero, Nexo and Pi Network
- OKX, Remitano and Revolut
- United States President Donald Trump
To maximize reach, the ads were localized in multiple languages — Vietnamese, Portuguese, Spanish, Turkish, Thai, Arabic, Chinese, and more.
|
Original Text |
Translated Text |
Language |
|
Tải ứng dụng chính thức Binance cho máy tính — phần thưởng 150 USDT sẽ được |
Download the official Binance desktop app — your 150 USDT bonus will be |
Vietnamese |
|
🖥 Plataforma de desktop avançada — sem complicação na instalação🔒 |
🖥 Advanced desktop platform — hassle-free installation🔒 |
Portuguese |
|
Alertas, indicadores, herramientas pro⚡ Rápido. Potente. Sin instalación⏳ |
Alerts, indicators, pro tools⚡ Fast. Powerful. No installation⏳ Full |
Spanish |
|
Dünya çapında 240 milyondan fazla kullanıcı tarafından güveniliyor |
Trusted by over 240 million users worldwide Download Binance for Windows |
Turkish |
|
🚨 คุณได้รับการแจ้งเตือนโบนัสจาก Binance! รับ $150 และใช้งาน |
🚨 You’ve received a bonus notification from Binance! Get $150 and |
Thai |
|
جرّب Binance على |
Try Binance on desktop and enjoy exclusive benefits — including a free |
Arabic |
|
📉 Harga normal $2.399,40/tahun – Sekarang Diskon 100%🚀 |
📉 Regular price $2,399.40/year – Now 100% Off🚀 Pro |
Indonesian |
|
免費高級 TradingView — 限時優惠!📉 原價 |
Free Premium TradingView — Limited Time Offer! 📉 Regularly |
Chinese (Traditional) |
In some cases, threat actors aligned brand lures with regional popularity, such as:
- Lemon.me in Latin America
- Exness and Orbix in Thailand
- Blackbull in Asia-Pacific
We have also observed examples in French, Bulgarian, Romanian and other languages.
This level of adaptation makes the campaign harder to spot and more convincing to its targets.


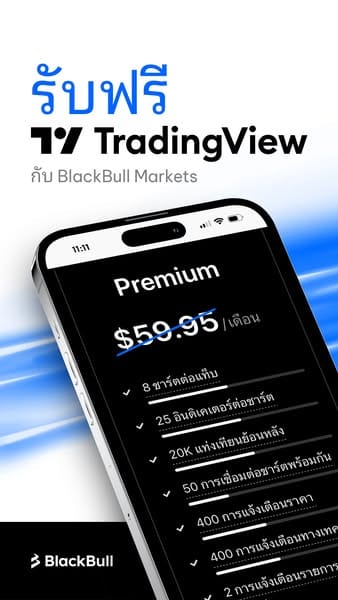
While the campaign targeting Windows users is ever-growing, at the time of writing, we’ve only found ads impersonating the Tradingview brand that are targeting Android users. Given past evolutions, we expect the number of ads and impersonated brands to increase. Interestingly, when accessing malicious domains specific to Windows from an iOS device, familiar content is shown, but it is also mentioned that the system is unsupported.

On Android, when accessing links specific to the Windows operating system, the displayed content is random and not tied to malicious advertisements in any way. The same happens with MacOS systems.
This expansion signals an alarming trend: mobile users are no longer safe from malvertising campaigns that once primarily targeted desktops. The combination of brand impersonation, localized ads, and sophisticated malware capabilities makes this campaign especially dangerous.
With the rise of mobile banking, crypto wallets, and 2FA apps on smartphones, the stakes are higher than ever. A single compromised Android device can hand over access to a victim’s finances, personal communications, and sensitive accounts.
Bitdefender detections for the campaign:
- Malware targeting Windows users are detected as Generic.MSIL.WMITask (MSI dropper) and Generic.JS.WMITask (front-end scripts)
- Android malware is currently detected as Android.Trojan.Dropper.AVV (dropper) and Android.Trojan.Banker.AVM (dropped malware).
How to Stay Safe
- Avoid sideloading apps – Only install apps from official stores like Google Play.
- Be wary of ads – Even on trusted platforms like Facebook, cybercriminals ca abuse ads.
- Check URLs carefully – Fake download pages often use lookalike domains.
- Review app permissions – If an app requests accessibility access or lock screen PINs without a clear reason, it’s a red flag.
- Use free scam detection tools from Bitdefender – Have a chat with Scamio (our AI-powered scam detector chatbot) or scan a suspicious link through Bitdefender Link Checker.
- Use a trusted security solution – Bitdefender Mobile Security for Android detects and blocks threats like Android.Trojan.Dropper.AVV and Android.Trojan.Banker.AVM before they can compromise your device.



